Showing metabocard for Hydrogen Ion (HMDB0059597)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Expected but not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2012-10-30 10:32:48 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2019-07-23 07:12:33 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0059597 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Hydrogen Ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Hydrogen Ion, also known as H+ or hydron, belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as other non-metal hydrides. These are inorganic compounds in which the heaviest atom bonded to a hydrogen atom is belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. Under aqueous conditions found in biochemistry, hydrogen ions exist as the hydrated form hydronium, H3O+, but these are often still referred to as hydrogen ions or even protons by biochemists. Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes. Hydrogen Ion is possibly neutral. Outside of the human body, Hydrogen Ion has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as sourdoughs, common grapes, lemon thymes, rowals, and sweet basils. This could make hydrogen ion a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | H | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 1.0079 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 1.007825032 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | hydron | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | hydron | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H+] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/p+1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | GPRLSGONYQIRFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as other non-metal hydrides. These are inorganic compounds in which the heaviest atom bonded to a hydrogen atom is belongs to the class of 'other non-metals'. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Other non-metal organides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Other non-metal hydrides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Other non-metal hydrides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Molecular Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Molecular Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MS/MS Spectra
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
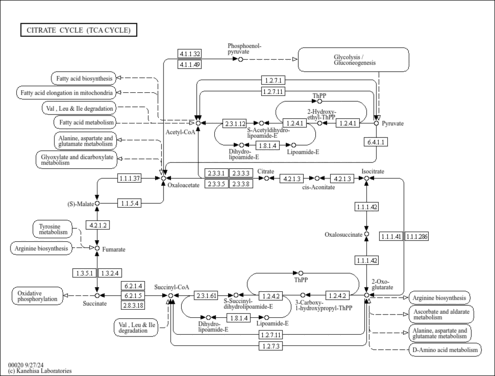
| Pathways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated Disorders and Diseases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disease References | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated OMIM IDs | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB030899 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 1010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Compound ID | C00080 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | PROTON | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Hydrogen ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound | 1038 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 15378 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VMH ID | H | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Good Scents ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 219 proteins in total.
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity
- Specific function:
- Fatty acid synthetase catalyzes the formation of long-chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH. This multifunctional protein has 7 catalytic activities and an acyl carrier protein.
- Gene Name:
- FASN
- Uniprot ID:
- P49327
- Molecular weight:
- 273424.06
Reactions
| Butyryl-[acp] + NADP → But-2-enoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (3R)-3-Hydroxybutanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + NADP → Acetoacetyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (3R)-3-Hydroxyoctanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + NADP → 3-Oxooctanoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (3R)-3-Hydroxypalmitoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + NADP → 3-Oxohexadecanoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (3R)-3-Hydroxytetradecanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + NADP → 3-Oxotetradecanoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Dodecanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] + NADP → trans-Dodec-2-enoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (R)-3-Hydroxyhexanoyl-[acp] + NADP → 3-Oxohexanoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Hexanoyl-[acp] + NADP → trans-Hex-2-enoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Octanoyl-[acp] + NADP → trans-Oct-2-enoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Decanoyl-[acp] + NADP → trans-Dec-2-enoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Tetradecanoyl-[acp] + NADP → trans-Tetradec-2-enoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Hexadecanoyl-[acp] + NADP → trans-Hexadec-2-enoyl-[acp] + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Plays a role in valine and pyrimidine metabolism. Binds fatty acyl-CoA.
- Gene Name:
- ALDH6A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02252
- Molecular weight:
- 57839.31
Reactions
| Malonic semialdehyde + Coenzyme A + NAD → Acetyl-CoA + Carbon dioxide + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Malonic semialdehyde + Coenzyme A + NADP → Acetyl-CoA + Carbon dioxide + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Malonic semialdehyde + Coenzyme A + NADP → Malonyl-CoA + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde + Coenzyme A + NAD → Propionyl-CoA + Carbon dioxide + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde + Coenzyme A + NAD → Methylmalonyl-CoA + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Lipoamide dehydrogenase is a component of the glycine cleavage system as well as of the alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Involved in the hyperactivation of spermatazoa during capacitation and in the spermatazoal acrosome reaction.
- Gene Name:
- DLD
- Uniprot ID:
- P09622
- Molecular weight:
- 54176.91
Reactions
| Dihydrolipoamide + NAD → Lipoamide + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Dihydrolipoylprotein + NAD → Lipoylprotein + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Enzyme N6-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine + NAD → Enzyme N6-(lipoyl)lysine + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Coenzyme A + NAD + Pyruvic acid → Carbon dioxide + Hydrogen Ion + NADH + Acetyl-CoA | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the transformation of the potent androgen dihydrotestosterone (DHT) into the less active form, 5-alpha-androstan-3-alpha,17-beta-diol (3-alpha-diol). Also has some 20-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity. The biotransformation of the pesticide chlordecone (kepone) to its corresponding alcohol leads to increased biliary excretion of the pesticide and concomitant reduction of its neurotoxicity since bile is the major excretory route.
- Gene Name:
- AKR1C4
- Uniprot ID:
- P17516
- Molecular weight:
- 37094.57
Reactions
| Androsterone + NAD → Androstanedione + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Androsterone + NADP → Androstanedione + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Etiocholanolone + NAD → Etiocholanedione + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Etiocholanolone + NADP → Etiocholanedione + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholestane + NAD → 7a-Hydroxy-5b-cholestan-3-one + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a,7a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholestane + NADP → 7a-Hydroxy-5b-cholestan-3-one + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 5beta-Cholestane-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-triol + NAD → 7a,12a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholestan-3-one + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 5beta-Cholestane-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-triol + NADP → 7a,12a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholestan-3-one + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Tetrahydrocortisone + NAD → 17a,21-Dihydroxy-5b-pregnane-3,11,20-trione + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 17a,21-Dihydroxy-5b-pregnane-3,11,20-trione + Hydrogen Ion + NADPH → Tetrahydrocortisone + NADP | details |
| Tetrahydrocortisol + NAD → Dihydrocortisol + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Tetrahydrocortisol + NADP → Dihydrocortisol + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a,11b,21-Trihydroxy-20-oxo-5b-pregnan-18-al + NAD → 11b,21-Dihydroxy-3,20-oxo-5b-pregnan-18-al + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a,11b,21-Trihydroxy-20-oxo-5b-pregnan-18-al + NADP → 11b,21-Dihydroxy-3,20-oxo-5b-pregnan-18-al + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Tetrahydrocorticosterone + NAD → 11b,21-Dihydroxy-5b-pregnane-3,20-dione + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Tetrahydrocorticosterone + NADP → 11b,21-Dihydroxy-5b-pregnane-3,20-dione + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a,21-Dihydroxy-5b-pregnane-11,20-dione + NAD → 21-Hydroxy-5b-pregnane-3,11,20-trione + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a,21-Dihydroxy-5b-pregnane-11,20-dione + NADP → 21-Hydroxy-5b-pregnane-3,11,20-trione + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a-Hydroxy-5b-pregnane-20-one + NAD → 5a-Pregnane-3,20-dione + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 3a-Hydroxy-5b-pregnane-20-one + NADP → 5a-Pregnane-3,20-dione + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Dihydrotestosterone + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion → Androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol + NADP | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- NADPH-dependent reductase with broad substrate specificity. Catalyzes the reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl compounds including quinones, prostaglandins, menadione, plus various xenobiotics. Catalyzes the reduction of the antitumor anthracyclines doxorubicin and daunorubicin to the cardiotoxic compounds doxorubicinol and daunorubicinol. Can convert prostaglandin E2 to prostaglandin F2-alpha. Can bind glutathione, which explains its higher affinity for glutathione-conjugated substrates. Catalyzes the reduction of S-nitrosoglutathione.
- Gene Name:
- CBR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16152
- Molecular weight:
- 30374.73
Reactions
| Prostaglandin F2a + NADP → Prostaglandin E2 + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion → 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol + NADP | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Has low NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase activity towards 4-benzoylpyridine and menadione (in vitro).
- Gene Name:
- CBR3
- Uniprot ID:
- O75828
- Molecular weight:
- 30849.97
Reactions
| Prostaglandin F2a + NADP → Prostaglandin E2 + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion → 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol + NADP | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- This is a copper-containing oxidase that functions in the formation of pigments such as melanins and other polyphenolic compounds. Catalyzes the rate-limiting conversions of tyrosine to DOPA, DOPA to DOPA-quinone and possibly 5,6-dihydroxyindole to indole-5,6 quinone.
- Gene Name:
- TYR
- Uniprot ID:
- P14679
- Molecular weight:
- 60392.69
Reactions
| Tyramine + Oxygen + NADH + Hydrogen Ion → Dopamine + NAD + Water | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols with a broad range of catalytic efficiencies.
- Gene Name:
- AKR1B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P15121
- Molecular weight:
- 35853.125
Reactions
| Glycerol + NAD → Glyceraldehyde + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Glycerol + NADP → Glyceraldehyde + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| beta-D-Galactose + NADH + Hydrogen Ion → Galactitol + NAD | details |
| beta-D-Galactose + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion → Galactitol + NADP | details |
| D-Xylitol + NADP → D-Xylose + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| L-Arabitol + NAD → L-Arabinose + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| L-Arabitol + NADP → L-Arabinose + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Sorbitol + NADP → alpha-D-Glucose + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Lactaldehyde + NAD → Pyruvaldehyde + NADH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
| Propylene glycol + NADP → Lactaldehyde + NADPH + Hydrogen Ion | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Desaturation and elongation of fatty acids, cholesterol biosynthesis, drug metabolism, and, in erythrocyte, methemoglobin reduction.
- Gene Name:
- CYB5R3
- Uniprot ID:
- P00387
- Molecular weight:
- 34234.55
Reactions
| NADH + ferricytochrome b5 → NAD + Hydrogen Ion + ferrocytochrome b5 | details |
Only showing the first 10 proteins. There are 219 proteins in total.